Now Reading: Determination of Age by Skull Suture
-
01
Determination of Age by Skull Suture
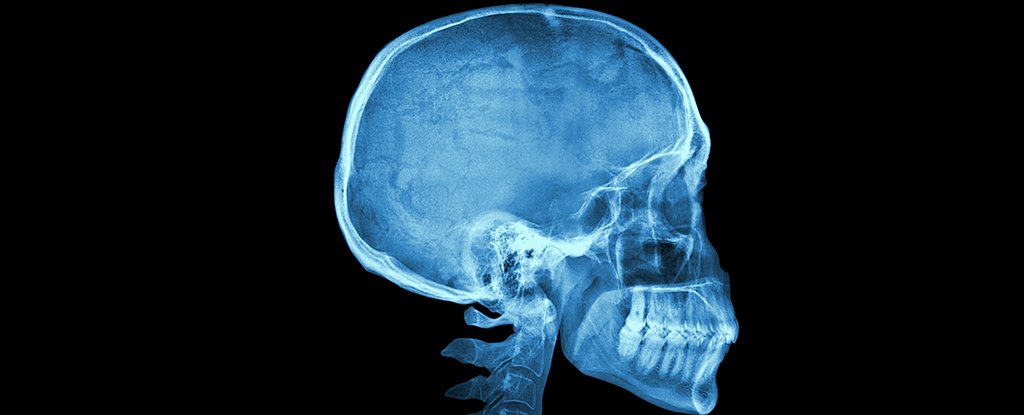
Determination of Age by Skull Suture
The determination of age by skull suture is a very essential work in the field of forensic anthropology. The forensic anthropology describes the scientific study of human skeleton remain and skull to determine age, sex and time of death to identify an individual. The identification is nothing but the recognition of an individual through various physical features or biological parameters there are many well-known parameters for identification of an individual such as any types of birthmarks, malformations, tattoo marks, scar, etc. these types of identification are done by the forensic anthropologist. The several decomposed bodies, burner disputed, mutilated are difficult to recognise their identification of an individual. The forensic anthropologist plays a crucial role in a death investigation in the field of forensic science. As a forensic anthropologist understand the form and variation of various form a of skeleton proportion and applied their knowledge to their work to obtain a reasonable conclusion.
The major suture of the skull including the following:-
1. Metopic suture:- this extends from the top of the head down the middle of the forehead towards the noise the two frontal bones plants meet at the metopic suture.
2. Coronal suture:- this extends form from ear to ear each frontal bone plate meets with a parietal bone plate at the coronal suture.
3. Sagittal suture:- this extends from the frontal of the head to the back down the middle of the top of the head the two parietal bone plates meet at the sagittal suture.
4. Lambdoid suture:- this extends across the back of the head each parietal bone plate meet the occipital bone plate at the lambdoid suture.
The determination of age by skull sutures is an integral part of the biological characteristics by a forensic anthropologist to assist in achieving the identification of an unidentified bodies individual. The determination of age through the study of various sutures can give us proper results.
Determination is one of the stiff problems in the medical justice system in both civil and criminal matters for such scenario like identification, senior becomes concession, juvenile offender, a determination is done by forensic experts and radiologists age determination by the skull sutures is the prominent method. As age increases it becomes a wide problem because of factors like nutrition, hereditary, racial, endocrine. In this method x-ray of both bone anterior-posterior and lateral view for the closer of suture, ecto-cranially is taken with certain measure sagittal, coronal, lambdoid, Prieto-mastoid, bass o-sphenoid sutures. The most successful estimate is done from sagittal suture, next lambdoid suture and then coronal suture. Identification means the determination of individuality of a person against in evidence of the skull for age determination because it is fused according to age since bones resist putrefaction this can lead to the reliable for determination of age, sex-based on morphological evidence.
Cranium sutures are one of the oldest and most controversial age indicators is cranial suture closure. suture closure by actually viewing the stage of the closure of suture of autopsy dead body, to see the actual fusion we can detect the age of decreased and ensure the time of death. Ectocranial sutures help to determine the age of decreased. Age is determined based on endocrinal suture fusion. Complete closure of sagittal suture occurs at the age of 61 to 65 years, almost complete closure of coronal suture occurs at the age of 56 to 60 years and almost complete closure of lambdoid, Temporoparietal suture occurs at the age of 66 to 70 year.
Let’s talk about how the skull develops inside in child paediatric skull is challenging, the stages of its evolution of skull are hard to find the answer of development and periods for radiologists. This difficulty stems from the variable nature and changing appearances of sutures over the normal developmental period. Sutures are some type of fibrous joint that occurs only in the skull. Synchronousness, which are also found in the skull, it is a type of hyaline cartilage joint. In an infant, large sutures—the sagittal, coronal, lambdoid, and squamosal sutures—are seen (less than 1 year of medical toddlers (aged 1–4 years) and persist into adulthood. Typically around the age of 22 years, the sagittal suture is the first to close. Around the age of 24 years, the coronal suture closes; and the lambdoid and squamosal sutures close at around 26 and 60 years, Premature fusion with osseous bridging is possible in all of these sutures. This phenomenon is known as craniosynostosis and changes the growth pattern of the skull, often resulting in an irregularly shaped cranium thus it stiff to find skulls sutures varying images in CT scan. The development of suture includes the innominate, metopic, medical, sphenosquamosal, sphenofrontal, and occipitomastoid sutures. Metopic suture closes by 3 months of age, and it should close in nearly all patients by 9 months. The sphenosquamosal suture typically closes by 6 years of age but can take as long as 10 years. The sphenofrontal and occipitomastoid sutures typically close at approximately 15 and 16 years of age. Types of sutures include metopic suture also known as the frontal suture, coronal suture remains unfused throughout childhood, typically closing by 24 years of age. Forensic science needs skull sutures method for age determination as because it is the prominent way to tell the real age of persons instead using birth certificates or Identity card. Ectocranial suture pattern can evaluate actual age. Bones are alive and carry all life functions. The condition of bones can tell an investigator about a person’s how old this person is and give a relevance result in age determination.
Author :- Vijay Panchal, Intern at Legal Desire (2020)
BSc. (H) Forensic Science, SAGE University, MP