Now Reading: Tenant Rights in India: 7 Must-Know Rules to Protect Your Rent & Agreement (State-Wise Guide)
-
01
Tenant Rights in India: 7 Must-Know Rules to Protect Your Rent & Agreement (State-Wise Guide)

Tenant Rights in India: 7 Must-Know Rules to Protect Your Rent & Agreement (State-Wise Guide)
Renting a home can be a fantastic experience, giving you flexibility and access to different communities. But understanding your rights as a tenant in India is crucial. No one wants a surprise rent hike or an unfair eviction notice. This guide breaks down essential rules and state-specific information to help you secure your rental agreement and live comfortably. Think of it as your go-to resource for a stress-free renting experience.
Secure Your Rent Agreement: 7 Key Tenant Rights
These aren’t just suggestions – they’re legally binding rights. Make sure your agreement reflects these:
- Written Agreement is Key: Always insist on a written rental agreement. It’s the foundation of your protection and outlines responsibilities. It spells out the rent amount, duration of stay, security deposit details, and other crucial terms.
- Fair Rent & Security Deposit: State laws often cap the security deposit amount (usually 2-3 months’ rent). Be aware of these limits and negotiate fairly. Unjustified demands are a red flag.
- Receipts are Your Proof: Always get receipts for rent payments. Keep a record of everything you pay. Digital payments offer easy tracking, but a formal receipt is always beneficial.
- Privacy Matters: Landlords can’t barge into your rented space unannounced. Except in emergencies, they must provide reasonable notice (usually 24 hours) before visiting.
- Essential Repairs: Your landlord is responsible for maintaining the property’s basic habitability – structural repairs, plumbing, and electrical issues. If they fail to address these, you might have grounds to take legal action or even deduct the repair cost from the rent (after proper notice).
- Protection Against Unfair Eviction: Landlords can’t evict you without a valid reason and proper legal process. They must serve a written notice period stipulated in your agreement or by state law. Reasons for eviction usually include non-payment of rent, property damage, or illegal activities.
- Right to Basic Amenities: You are entitled to basic amenities like water and electricity. Disrupting these services is illegal and can be contested.
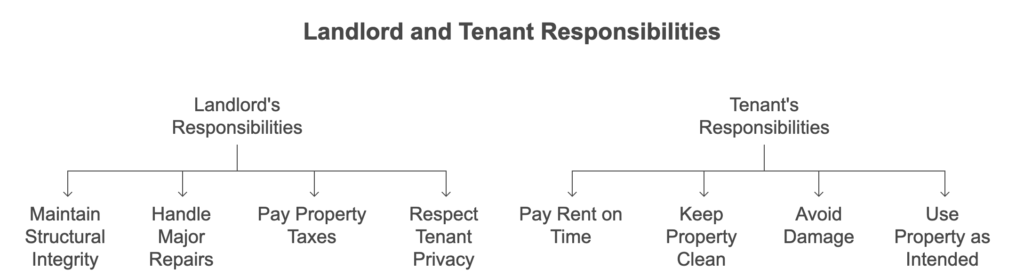
Landlord Responsibilities vs. Tenant Rights: Knowing the Difference in India
Think of it as a partnership: both parties have duties.
- Landlord’s Job: Maintaining structural integrity, handling major repairs, paying property taxes, and respecting tenant privacy.
- Tenant’s Job: Paying rent on time, keeping the property clean, avoiding damage beyond normal wear and tear, and using the property for its intended purpose (residential, not commercial, unless agreed upon).
For example, if the roof leaks, that’s the landlord’s responsibility. If you break a window, that’s generally yours. Clear communication is key to avoiding conflicts.
Rent Control Laws in India: A State-Wise Overview of Tenant Protection
Tenant laws vary significantly by state. These variations reflect differences in local real estate conditions and housing policies.
- Model Tenancy Act (MTA): While not directly enforceable, the MTA provides a template for states to modernise their laws. Several states are in the process of adopting or adapting it. It seeks to balance tenant and landlord interests.
- Maharashtra: Known for strong tenant protections, especially in older buildings with rent control. However, new constructions are generally exempt.
- Tamil Nadu: Relatively balanced laws, emphasising agreements and clear eviction procedures.
- Delhi: The Delhi Rent Control Act is still in effect but is being updated to align with modern needs.
- Karnataka: The Karnataka Rent Act offers more protection to tenants compared to some other states, with specific regulations on rent increases.
Important: Always research the specific rent control act applicable to your state. Websites of state governments usually offer downloadable versions of these acts.
Avoiding Disputes: Safeguarding Your Rights as a Tenant
Prevention is better than cure.
- Document Everything: Take photos/videos of the property’s condition before moving in. This prevents disputes about pre-existing damage when you move out.
- Communicate in Writing: Keep a written record of all communication with your landlord, especially regarding repairs or issues with the property.
- Pay Rent on Time: This is your most basic obligation. Late payments can give the landlord grounds for eviction.
- Know Your Rights: Familiarise yourself with your state’s rent control laws and rental agreement terms.
- Negotiate Fairly: If a dispute arises, try to resolve it amicably with your landlord. Mediation can be a helpful alternative to legal action.
Breaking the Lease? Understand Your Tenant Rights and Exit Strategies
Life happens. Sometimes you need to move before the lease ends.
- Review Your Agreement: Check the lease for clauses about early termination. It might specify penalties or procedures for breaking the lease.
- Negotiate with Your Landlord: Talk to your landlord and explain your situation. They might be willing to waive penalties or allow you to find a suitable replacement tenant.
- Subletting: If your lease allows it, you can sublet the property to another tenant for the remainder of your lease term. However, you’re still responsible if the subtenant doesn’t pay rent or damages the property.
- Legal Grounds: In some cases, you might be able to break the lease without penalty if the landlord violates the lease agreement (e.g., fails to make essential repairs) or if the property becomes uninhabitable.
Key Resources for Tenants in India: Protecting Your Rights and Seeking Help
You’re not alone. Here’s where to find support:
- State Government Websites: Look for your state’s Department of Housing or Urban Development website.
- Legal Aid Societies: These organisations provide free or low-cost legal assistance to those who can’t afford it.
- Tenant Associations: Search for tenant associations in your area. They can provide information, advocacy, and support. Some examples include tenant unions in major cities like Mumbai and Bangalore. These groups often offer workshops and resources.
- Online Legal Platforms: Several websites offer legal advice and assistance online. Be sure to choose reputable platforms.
- Consumer Courts: You can file a complaint with a consumer court if you believe your rights as a tenant have been violated.
- Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA): While primarily focused on property buyers, RERA also offers some protections to tenants, especially regarding transparency and fair dealings.
Remember, knowing your tenant rights is your first line of defence. Stay informed, communicate effectively, and don’t hesitate to seek help when needed.