Now Reading: Good Samaritan Law India: From Motor Vehicle Act to Reality – 7 Things To Know Before Helping
-
01
Good Samaritan Law India: From Motor Vehicle Act to Reality – 7 Things To Know Before Helping

Good Samaritan Law India: From Motor Vehicle Act to Reality – 7 Things To Know Before Helping
Imagine witnessing a road accident. Your instinct screams at you to help, but fear holds you back. What if you get entangled in legal hassles? What if the police harass you? This is a common dilemma in India, where the “bystander effect” can be tragically strong. But fear not! The Good Samaritan Law in India aims to protect those who step forward to assist accident victims. Here’s what you need to know.
What is the Good Samaritan Law India and Why Should You Care?
The Good Samaritan Law isn’t a single, standalone piece of legislation. Instead, it’s a set of guidelines and provisions designed to protect individuals who assist accident victims in good faith. It aims to encourage bystanders to offer help without fear of legal repercussions or harassment. Why should you care? Because your intervention could save a life. Every minute counts in a medical emergency, and your timely assistance can make all the difference. By understanding your rights and protections under the law, you can act confidently and potentially save someone’s life without jeopardizing your own well-being.
In India, road accidents claim a staggering number of lives annually. According to the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, in 2022 there were over 460,000 road accidents, resulting in over 168,000 deaths. A significant percentage of these deaths occur because victims don’t receive timely medical assistance. The Good Samaritan Law is crucial to address this issue.
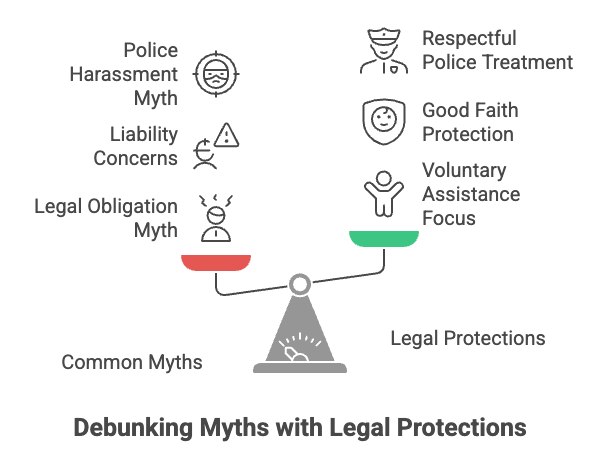
Good Samaritan Law India Explained: Debunking the Myths
Many misconceptions surround the Good Samaritan Law in India. Let’s clear some up:
- Myth: You’re legally obligated to help. There is no legal obligation to assist an accident victim. The law focuses on protecting those who choose to help voluntarily.
- Myth: You’ll be held liable if something goes wrong. The law provides protection for acts done in good faith. If you act reasonably and without negligence, you won’t be held liable, even if the victim’s condition worsens.
- Myth: The police will automatically harass you. The law mandates that police officers treat Good Samaritans with respect and avoid unnecessary questioning or detention.
- Myth: You have to stay until the entire process is complete. While providing information to the police is helpful, you are not required to stay at the police station unnecessarily.
The core principle is acting in “good faith.” This means you’re genuinely trying to help, not acting recklessly or with malicious intent.
Good Samaritan Law India Motor Vehicle Act: The Road to Protection
The Good Samaritan Law in India is deeply intertwined with the Motor Vehicle Act. The Act has been amended to incorporate provisions that safeguard Good Samaritans. This amendment was a crucial step in solidifying the legal protections for those who offer assistance to accident victims.
Previously, there were no specific legal protections for bystanders who assisted road accident victims. This often led to reluctance among the public to come forward due to fears of legal harassment, police questioning, and potential liability. The amendment to the Motor Vehicle Act brought about a significant change, ensuring that Good Samaritans are not penalized for their actions and are treated with respect by authorities. This has been particularly impactful in states with high accident rates, like Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh, where increased awareness of the law has encouraged more people to assist accident victims.
Supreme Court Guidelines Good Samaritan Law India: A Landmark Judgement
The Supreme Court of India played a pivotal role in establishing and reinforcing the Good Samaritan Law. In 2016, the Supreme Court endorsed the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, making them legally binding across the country. This landmark judgement provided a strong legal basis for protecting Good Samaritans and promoting bystander intervention.
The Supreme Court’s endorsement of the guidelines sent a clear message that the safety and well-being of accident victims should be prioritized. It reinforced the idea that individuals who come forward to help should not face legal or administrative hurdles. This ruling had a positive impact on the ground, encouraging more people to assist accident victims without fear of legal repercussions. For instance, studies have shown a gradual increase in bystander intervention rates in cities like Delhi and Mumbai following the Supreme Court’s decision.
Is There a Good Samaritan Law in India? Clearing the Confusion
Yes, there is a Good Samaritan Law in India, but it’s not a single, codified law. It exists as a combination of guidelines, Supreme Court rulings, and amendments to the Motor Vehicle Act. This multifaceted nature can cause confusion. The important takeaway is that these provisions do offer legal protection to those who help accident victims in good faith. The key is to be aware of these protections and exercise your rights accordingly.
Understanding the Bystander Effect in India and the Law’s Role
The “bystander effect” describes the phenomenon where individuals are less likely to offer help in an emergency when others are present. The presence of other bystanders creates a diffusion of responsibility, where each person feels less personally responsible for taking action. This is a significant issue in India, where a combination of factors, including fear of legal hassles, police harassment, and lack of awareness about the Good Samaritan Law, contributes to the bystander effect.
The Good Samaritan Law plays a crucial role in mitigating the bystander effect by providing legal protection and encouragement for people to step forward and help. By assuring individuals that they won’t be penalized for their actions, the law reduces the fear and uncertainty that often prevent people from intervening. This proactive approach is essential to counter the bystander effect and increase the likelihood of timely assistance for accident victims.
Seven Things You MUST Know Before Helping an Accident Victim in India
Here are seven key things you should know before helping an accident victim in India:
- Your Identity: You cannot be compelled to disclose your name and personal details to the police or at the hospital unless you are a witness to the accident.
- Hospital Payments: Hospitals cannot detain you or demand payment before providing immediate medical care to the victim. Public hospitals are obligated to provide free treatment.
- Police Questioning: Police are required to treat you with respect and avoid unnecessary questioning. They should not pressure you to become a formal witness.
- Confidentiality: You have the right to request that your identity be kept confidential during legal proceedings.
- Protection from Liability: You are protected from civil and criminal liability for any unintentional harm caused while providing assistance in good faith. This means that as long as you act reasonably and without negligence, you cannot be held responsible if the victim’s condition worsens.
- Rewards and Recognition: The government may offer rewards and recognition for Good Samaritans to encourage more people to come forward and help. While not consistently implemented across all states, initiatives like these aim to acknowledge and appreciate the efforts of those who assist accident victims.
- Reporting Mechanism: Familiarize yourself with local reporting procedures. Document the incident, time, location, and actions taken, and report the incident to the authorities. Ensure the hospital and police are aware you are acting under the ‘Good Samaritan’ guidelines to avail protection.
- Abuse Prevention: If you suspect abuse of the law, report it to the relevant authorities, such as the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) or the State Human Rights Commission (SHRC).
Further Considerations:
- Training Programs: Look for first aid and basic life support training programs in your area. These programs can equip you with the necessary skills and knowledge to provide effective assistance to accident victims. Organizations like the Indian Red Cross Society and St. John Ambulance offer courses that can prepare you to handle emergency situations confidently.
- Legal Challenges and Loopholes: Despite the protections offered by the Good Samaritan Law, there can still be challenges and loopholes in its implementation. Some police officers and hospital staff may be unaware of the law or may not fully adhere to its provisions. In such cases, it’s important to assert your rights and, if necessary, seek legal assistance.
- Comparison with Other Countries: Good Samaritan laws exist in many countries around the world, but their specific provisions vary. For example, in some countries, there may be a legal duty to rescue, while in others, the focus is solely on protecting volunteers who provide assistance. Understanding the differences in these laws can provide valuable insights into best practices for promoting bystander intervention.
- Case Studies and Successful Implementations: There are several case studies that highlight the successful implementation of the Good Samaritan Law in India. For instance, in some cities, increased awareness campaigns and training programs have led to a significant increase in bystander intervention rates and a reduction in accident fatalities. Sharing these success stories can inspire and motivate others to take action in similar situations.
By understanding these seven crucial points, you can confidently act as a Good Samaritan, potentially saving a life while safeguarding yourself. Don’t let fear paralyze you. Be informed, be prepared, and be ready to help.