Now Reading: Radiomics in Forensic Examination
-
01
Radiomics in Forensic Examination

Radiomics in Forensic Examination
Abstract
Radiomics is an ‘imaging analytics’ technique emerging in the field of applied radiology. A new frontier in clinical decision-making with diagnosis and prognosis. But it also extended its hands over to crime investigation. Examination of charred bones can be carried using ‘Radiomics’. It can determine the time interval of combustion and, hence, even the attempt to wash out the evidence can solve the case with improved technology.
Keywords: Combustion, Burnt bone, Micro-CT, Radiology, Radiomics features
Introduction
The field of medical image analysis has greatly evolved during the last decade, with a significant increase in the number of pattern recognition techniques and improvement in current ones. Radiomics is the field of medical imaging analysis that extracts feature information from images using data characterization algorithms. Radiomics features are obtained from medical images using different techniques like CT scan, MRI scan, etc. the quantitative elements of Radiomics can be detected using special software which requires medical images as a source. The processes of Radiomics can be divided into different stages, (i) image acquisition (ii) image segmentation (iii) feature extraction (iv) analyses.
New crime investigator: Radiomics
Radiomics, the process which collects data from medical images, can be used in the examination of charred bones without any doubt. It is critical in forensic casework to have accurate information from fragments of burnt bones to determine the victim. Burning of bones results in physical as well as chemical changes which can complicate DNA and anthropological tests and even give out false test results when examined. Due to shrinking during the process of burning, heat exposure can cause bones to distort and fragment, which can cause changes in the morphological features that are crucial for forensic anthropology analysis, such as identification of species, gender, age, and estimation of stature. Heat induces chemical changes in bones along with the physical changes as a result of combustion and pyrolysis of chemical compounds during the process of burning. To determine and analyse the changes in the bone and its structure due to exposure to fire and to estimate the time interval of combustion, Radiomics, is the best innovation so far; according to the study conducted by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) on charred Human bones. The details of the study was presented at the106th annual meet of RSNA
Considering the field of forensic science, details of combustion in cases where combustion is used as concealment for murders. Therefore, a reliable examination method for such cases aids in forensic investigation to solve the case. Radiomics assesses the timely changes in human bone samples which are exposed to temperature and fire and gives add-on information such as establishing the time interval between the processes of combustion.
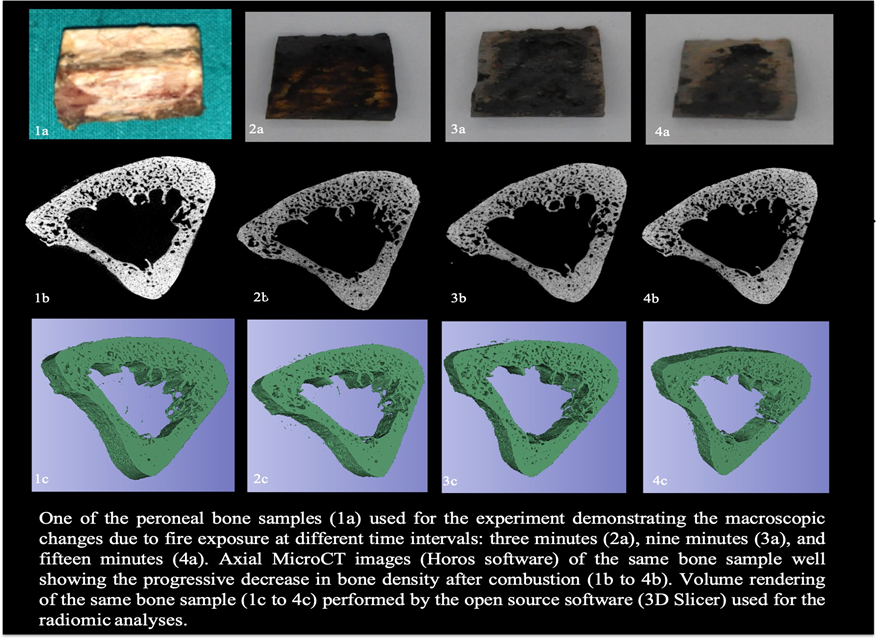
In the experiment conducted by the RSNA, the researchers studied the samples using high-resolution images from a micro-CT scan to examine about 15 samples. Samples were examined before and after exposure to fire. Different characteristics such as volume and density of the samples were analysed.
According to the researchers, Radiomics is capable to determine the changes in the bone samples depending on the time of exposure to the fire. This research evaluates the significance of Radiomics in defining the variations in human bone samples when exposed to fire based on the time interval and suggests a method for collecting additional information for determining the time and cause of death of the victim.
Radiomics can be applied to a wide range of imaging techniques, including radiographs, ultrasound, and CT, MRI, and PET scans. It can be used to increase the accuracy of diagnosis, assessment of prognosis, and other applications in the clinical and biochemical areas. The technique has been used in oncological studies, particularly for breast and lung cancer, but it can potentially be applied to any disease. The concept of Radiomics is motivated by the idea that biomedical images contain information that reflects underlying pathophysiology and that these links can be revealed through quantitative image analyses. Although Radiomics is a natural extension of computer-aided diagnosis and detection (CAD) systems, it is significantly different from them.
The goal of Radiomics is to extract as much information as possible from standard-of-care images. As far as Forensics is considered, Radiomics can be useful for interrupting fundamental details in charred bone examinations. Heat exposure increases the difficulties in charred bone, depending on the exposure temperature. The role of Radiomics is to provide information that will assist forensic scientists in interpreting and analysing the results obtained from Radiomics of charred bones more accurately.
Burnt bones in forensics
Charred bones are examined in the forensic laboratory as evidence in a variety of cases, such as road accidents where the vehicle is burned, natural or any kind of disasters, house fires, and accidental industrial fires. In addition to vehicle cases, an investigator can find cases for example homicide cases where the body is cremated and destroyed to wash out the leading evidence and to obstruct the investigation.
The artificial crushing of charred bones, followed by heat-induced fragmentation, makes forensic anthropological examinations difficult. Furthermore, one of the main analysis for individual identification; DNA extraction of severely burned bones can be difficult. The burning process also reduces the volume of bone. Volume and density change are some of the significant changes in burnt bones, CT analysis produces reliable results of the samples examined about its volume and density. The volume does not change until the temperature reaches 600°C but then decreases significantly after this temperature till 1,100°C. At this point, the volume of the bone is nearly halved.
Challenges
Radiomics is a new field with significant challenges in implementing it in a clinical setting. Each process possesses unique challenges. Current challenges include recording of high-quality images with resolution (pixel size or matrix size and slice thickness), sharing difficulties of these high-resolution data images, large computing power, and need large storage capacity. The process of the acquisition of images is time-consuming and costly.
Conclusion
Radiomics is a process which has different levels as mentioned above that helps in clinical aspects and prediction, which holds the last position in the list of most amazing innovations in the field of medical science, especially in imaging analysis. Not only in medicine but also in forensic, Radiomics have its role. Both qualitative and quantitative information can be extracted from the images developed using technique such as CT scans and MRI scans. Even though Radiomics has demonstrated its ability for diagnosing and prediction purposes in several studies, the field is facing many challenges. Each has its own set of challenges that must be overcome.
References
- RSNA 2020: Radiomics Aid Forensic Examination of Charred Human Bones. (2020). Applied Radiology. https://appliedradiology.com/communities/Artificial-Intelligence/rsna-2020-radiomics-aid-forensic-examination-of-charred-human-bones
- Dove Press. (2015, December 10). Forensic investigation of burnt human remains | RRFMS. Dovepress. https://www.dovepress.com/forensic-investigation-of-burnt-human-remains-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-RRFMS#
- Researchers Use Radiomics in Forensic Examination of Charred Human Bones. (2020, December 9). Forensicmag.Com. https://www.forensicmag.com/571004-Researchers-Use-Radiomics-in-Forensic-Examination-of-Charred-Human-Bones/
- Idris, M. (2017, November 13). Radiomics | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Radiopaedia. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/radiomics
- Radiomics: the facts and the challenges of image analysis. (2018, November 14). PubMed Central (PMC). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6234198/
- Mayerhoefer, M. E. (2020, April 1). Introduction to Radiomics. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. https://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/61/4/488
- The image shows the changes in bones due to fire exposure. (n.d.). [Photograph]. The Image Shows the Changes of Bones Due to Fire Exposure. https://cdn.agilitycms.com/applied-radiology/Images/charred%20bone.jpg
- Timmeren, J. V. E. (2020, August 12). Radiomics in medical imaging—“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights into Imaging. https://insightsimaging.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s13244-020-00887-2