Now Reading: Types of Injuries and their Medico-Legal aspects
-
01
Types of Injuries and their Medico-Legal aspects
Types of Injuries and their Medico-Legal aspects
An injury is defined as the termination of the natural continuity of any of the tissues of the living body. According to Section 44 of the Indian Penal Code, injury is defined as any harm caused illegally to a person i.e. to his body, mind, reputation or property.
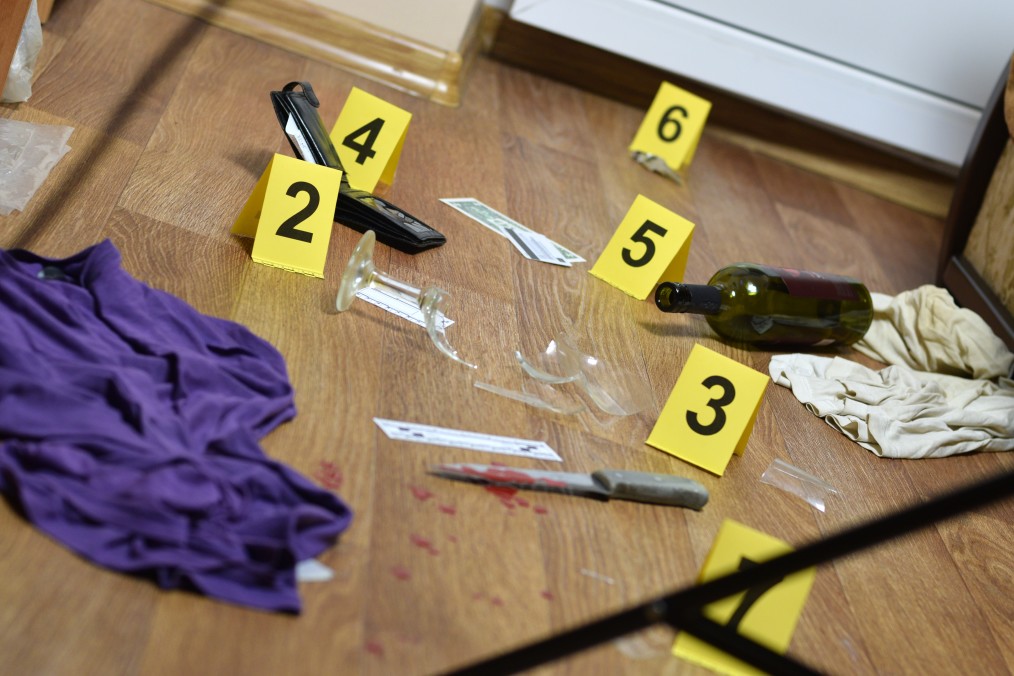
There are different classifications given for injuries. The etiological classification categorizes injuries as two kinds: mechanical and thermal. Mechanical injuries are sub-classified into abrasions, contusions, lacerations, stab injury, incised wounds and firearm injuries. Thermal injuries are sub-classified into burns and scalds, frostbite, chemical burns, radial burns and electric burns. Medico-legal classification is based on three grounds: severity, mode of death and moment of death. Injuries based on severity: simple and grievous injuries, based on mode of death: suicidal, homicidal and accidental injuries and based on moment of death: ante-mortem and postmortem.
Incised injuries are made by sharp edged weapons and have clear cut separation of tissues. Length of the injury is greater than the depth. The medico legal importance of incised wounds are:
1. The nature of weapon can be confirmed to be sharp edged.
2. Determination of the age of injury was possible.
3. The direction of application force can be determined from the tail of the wound.
4. Homicidal incised wounds are frequent.
Abrasion injuries are blunt force injuries and results in the destruction of superficial layers of epidermis. A pure abrasion rarely bleeds and it is a two dimensional injury. The medico legal significances are as follows:
1. Age of the injury can be determined.
2. Pattern abrasion can help us identify the type of weapon used.
3. Abrasions on the face of suspect can indicate struggle.
4. Suicidal abrasions are rare. They are often seen in accidents and homicides.
Lacerations are tearing or splitting of skin, mucous membrane or internal organs. This is caused by blunt force on the body tissue or skin. Lacerations are three-dimensional and the margins are uneven and irregular. Following are the medico legal aspects:
1. These injuries can indicate the shape of the blunt weapon.
2. Determining age in uninfected lacerations is quite useful.
3. Foreign bodies found in the wound site might help us reconstruct the circumstances during the commission of crime.
4. These wounds are generally seen in accidents and assaults.
5. Lacerations are generally considered grievous injuries.
Stab wounds are mechanical injuries where the depth is the greatest dimension when compared to the length and breadth. They can be produced by knives, dagger and sword. The medico legal aspects of such wounds are:
1. Stab wounds are majorly homicidal or suicidal. Accidental wounds are very infrequent.
2. The depth of the wound shall signify the penetration force.
3. Age of the injury can be estimated.
4. Shape of the wound helps to classify the type and class of weapon. For example, the length, width and thickness of the weapon, whether it is single edged or double edged are the characteristics studied.
Burn injuries are those that are produced on the body by the application of dry heat like flame, fire or radiation. Medico-legal aspects of this category of injury are:
1. Presence of smoke in the respiratory passage of the victim indicates he or she was alive when fire started.
2. Raised carboxyhaemoglobin in the blood. The percentage often exceeds 10%.
3. Presence of red line in the region adjacent to the burns.
A contusion is an effusion of the blood into the tissue due to the rupture of vessels, especially capillaries. They are caused as a result of blunt force trauma.
1. Self-inflicted bruises are rare.
2. Contusions can be homicidal, suicidal or accidental.
3. Shape and size of bruise is similar to the nature of the weapon.
4. Age of the injury can be determined.
Firearm wounds include both the entrance and exit wounds. The wounds vary in shape and size depending on the range of shooting, velocity of projectile and target site. Medico-legal aspects of firearm injuries include:
1. Suicidal firearm wounds are often indicated by the firearm in the hands of the victim due to cadaveric spasm.
2. Accidental firearm injuries are rare in occurrence.
3. Nature of the firearm can be determined. For instance, whether it is smooth bore or rifled.
4. Homicidal or suicidal injuries are common.
5. Range and direction of firing can be calculated.
When electric current passes through the body, it causes various effects such as muscular spasms, contact burns or severe charring. These are the effects of electrocution and some of their medico-legal aspects are:
1. Suicidal electrocution is rare but might occur in mentally unsound people.
2. Homicidal electrocutions are more frequent. Electrocution via occurs through accidents.
For instance, circuit may pass through any of the limbs to the head and lead to paralysis of respiratory centre.
3. The site of entrance may be diagnosed histochemically by seeing deposition of metal particles on the skin.
4. An arm to arm circuit or left arm to either leg involves heart. Death occurs due to ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest without fibrillation.
Simple injury or hurt causes bodily pain, disease or infirmity to any person for a short period and it does not endanger life. On contrary, grievous hurt is caused by certain conditions as mentioned under Section 320 of IPC.
Under Section 320 of IPC, grievous hurt is constituted by the following:
1. Emasculation
2. Losing the ability to see by either eye permanently
3. Losing the power of hearing of either ear permanently
4. Privation of any member or joint
5. Destruction or permanent impairment of power of any member or joint
6. Deformation of head or face permanently
7. Bone or tooth getting fractured or dislocated
8. Any hurt which endangers life or which causes severe pain to the individual or he is unable to do his daily activities for 20 days
Emasculation is depriving a male of his masculine vigor.
Permanent loss of sight of either eye not only means lacking the function of a vital organ in the body but also deforming the person. It can be caused by poking eyes or pouring chemicals over it.
Blow on the head or ear or affecting the tympanic membrane or auditory nerves can cause permanent privation of hearing in either ear.
Incapacity of a limb or organ which performs an individual and distinct action is known as privation of any member or joint.
Deprivation of the functions of any of the ability of any limb or joint makes a person a lifelong cripple or physically disabled, thus ruining the normal course of his life.
Disfigure does not mean making an individual incapable physically. It is causing external injuries that have consequences on his or her life. For instance, a scar on the face of an actress can lead to damage to her professional establishment.
Any break or discontinuity in the bone is considered to be a fracture. A bone need not break completely for it to be considered as a fracture. Dislocation means displacement of a tooth or bone from its normal anatomical position.
The injuries which do not fit into any of the aforementioned clauses are included in the eighth clause. An injury may cause serious body pain or might threaten an individual’s survival but does not come under any of the above conditions are included here.
The medico-legal opinion with respect to injuries should contain the whole description and an opinion regarding its legal state. These opinions help the court of law to decide the seriousness of the crime and also in sentence evaluation of the suspect.
References:
· https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269557204_Medicolegal_Aspects_of_Hurt_Injury_and_Wound
· https://www.slideshare.net/AkshayDeokar3/injury-forensic-science